leech
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners such as Chewy, Amazon, etc. These purchases help us further AZ Animals' mission of educating the world's species.
The leech (Hirudinea) is a predator and blood-sucking parasite native to almost every continent. This aquatic worm is a member of the phylum Annelida, which means it is related to earthworms.
Leeches have a bad reputation among humans. We consider them blood-sucking pests and use the word "leech" as an insult. However, most of them do not attack humans, and many do not feed primarily on blood. In ancient times, they were used medicinally. Today, doctors use medical leeches to clean delicate tissue during surgery.
Have you ever been hiking in the wet, or fishing in some wetlands, and found a leech attached to your calf later that day? It will send more than a few people screaming for help, while others may just shrug and pull it off. So what do you think when you start with a leech attached to your limb? Where do leeches live? Read on to learn more about these intriguing invertebrates, including the answer to this burning question.

© AZ-Animals.com
5 Amazing Leech Facts!
- They have 10 eyes but have very poor eyesight.
- They can go without food for 6 months.
- Leeches live on every continent except Antarctica.
- Some people use them as bait.
- Leech therapy is a recognized medical practice.
scientific name
© Martin Pelanek/Shutterstock.com
The scientific name of the leech is Hirudinea. There are more than 680 different species or types of leeches. Of these, 100 were saltwater leeches, 480 were freshwater leeches, and the rest lived on land. Terrestrial leeches usually live on the banks of ponds and lakes. They are invertebrates belonging to the phylum Annelids, the phylum that includes earthworms.
The scientific name comes from the word hirudin. Hirudin, a peptide naturally found in the salivary glands of blood-sucking leeches, prevents blood from clotting.
Types of leeches
- Kinabalu Giant Red Leech – The Kinabalu Giant Red Leech definitely lives up to its name. The insects are bright reddish-orange and 20 or more inches long. It was found on a mountain in Borneo. The Kinabalu giant red leech is a carnivore that eats a worm that lives in Borneo.
- Piscicola geometra – These leeches can be found in freshwater in North America and northwestern Europe, in stagnant and fast-moving water. They do prefer waters with high oxygen content.
- Hirudo medicinalis – Known as "medical leeches," these types of leeches can consume up to ten times their body weight in blood. They have a thin red stripe on their back.
- Americobdella Valdiviana – Americobdella valdiviana can be found in South America, especially in Chile. The presence of its eyes is disputed, this leech has a yellow front area and a gray back.
appearance
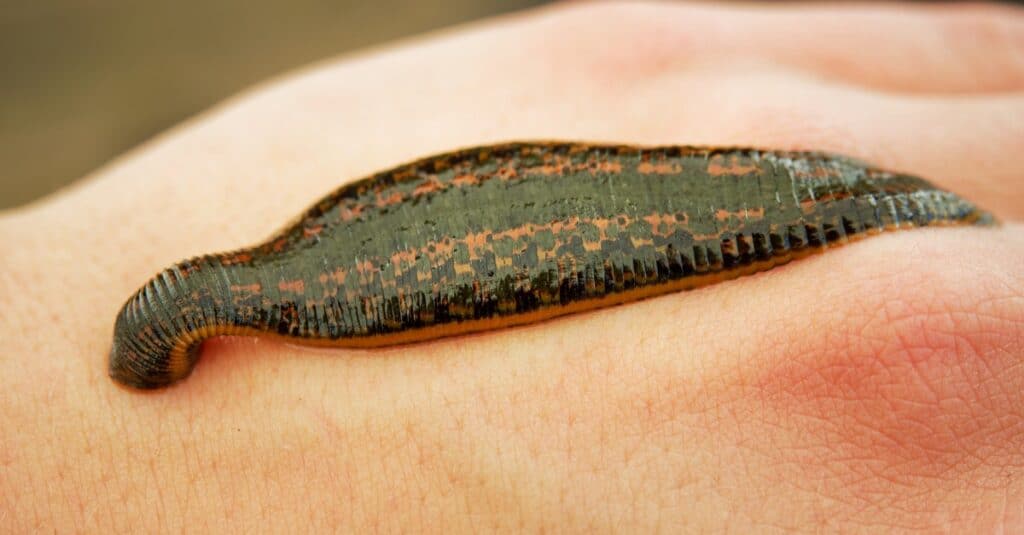
A leech looks like a fat, black, shiny earthworm. It has a solid segmented body with tapered ends and a pair of suction cups at each end. The leech uses its suckers to attach itself to the animal's skin and suck its blood.
Leeches usually have two or three rows of small teeth. The small size of these teeth is part of the reason you don't feel the leech bite.
The body of a leech is usually a dark greenish-brown color without spots or stripes. Some are so dark they look black. Leeches vary in size, but a typical leech is 2 inches long. The largest species of leech is the giant Amazon leech ( Haementeria ghilianii ), which can be 18 inches long and 4 inches wide.
©Ronald Shimek/Shutterstock.com
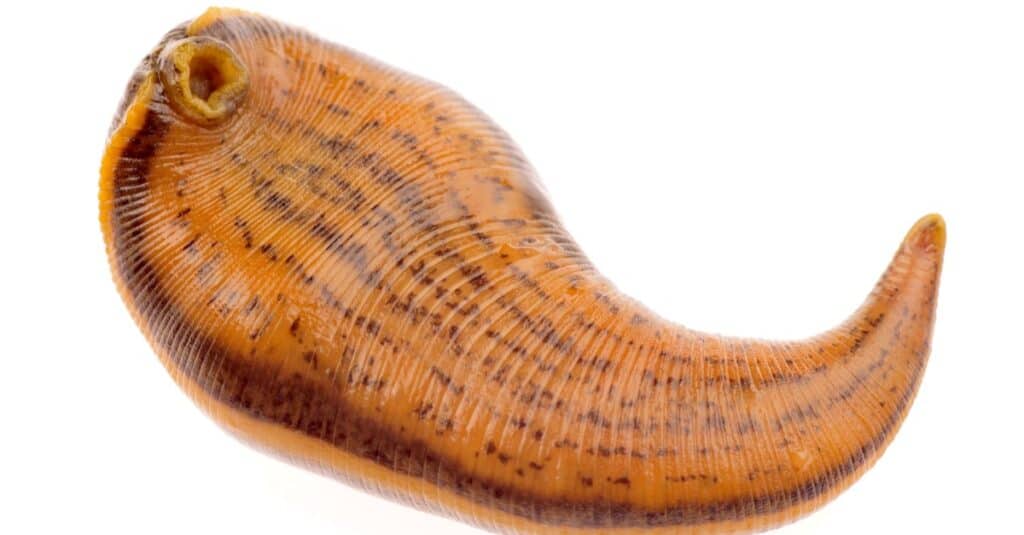
Behavior

©pan demin/Shutterstock.com
Leeches typically inhabit lakes and ponds and move slowly through the water in search of food. They do not form complex societies, but they can usually be found in groups.
Certain types of leeches are parasites and predators. They prey on insects and small aquatic animals, and also suck the blood of fish and warm-blooded animals. Their saliva contains an anticoagulant, which keeps the prey's blood flowing while being bitten, and an anesthetic, which prevents the prey from feeling the bite.
They are an important part of pond ecosystems, and some people who keep natural ponds in their gardens put leeches in them for this very reason. They are an important food source and clean up the droppings of dead animals. However, pond and fish farmers must be careful to use the correct type of leech. Some leeches inflict damage on fish by sucking blood, which can cause the fish to become sick or weak.
Leeches don't actively seek out people, but if you swim or wade in their territory, they will try to grab food.
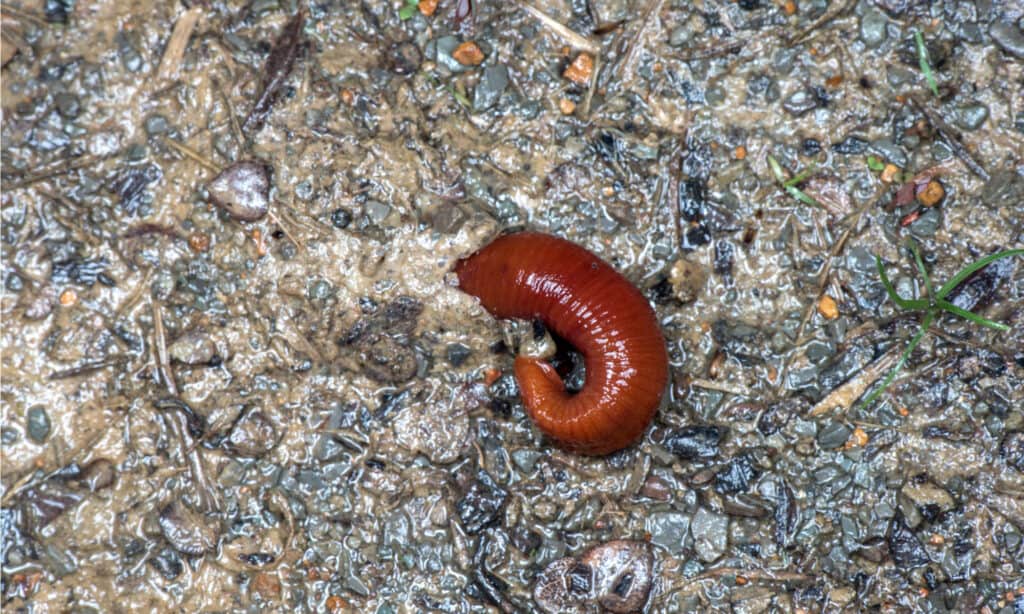
Habitat

©Norjipin Saidi/Shutterstock.com
Most types of leeches live in freshwater ponds and lakes. Their preferred habitat is warm, slow-moving waters. They do not do well in fast flowing streams or rivers. There are some saltwater leech species, but they mostly live in the depths of the ocean far from human habitation.
Although leeches prefer warm temperatures, they are extremely adaptable to their environment. They can go without food for long periods of time and will adjust their body temperature according to the current environment. That's why they're everywhere except in the frozen regions of Antarctica.
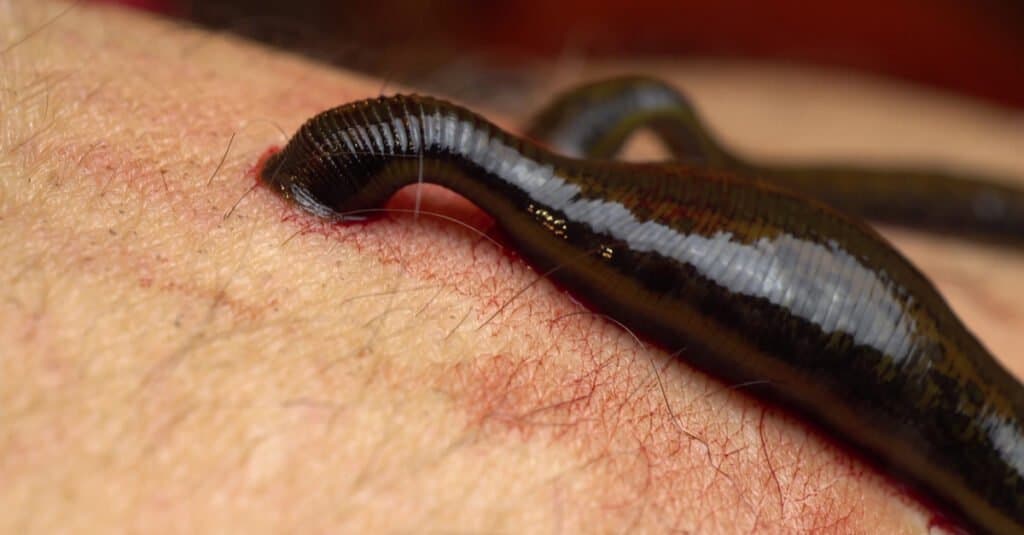
diet

©Vital9s/Shutterstock.com
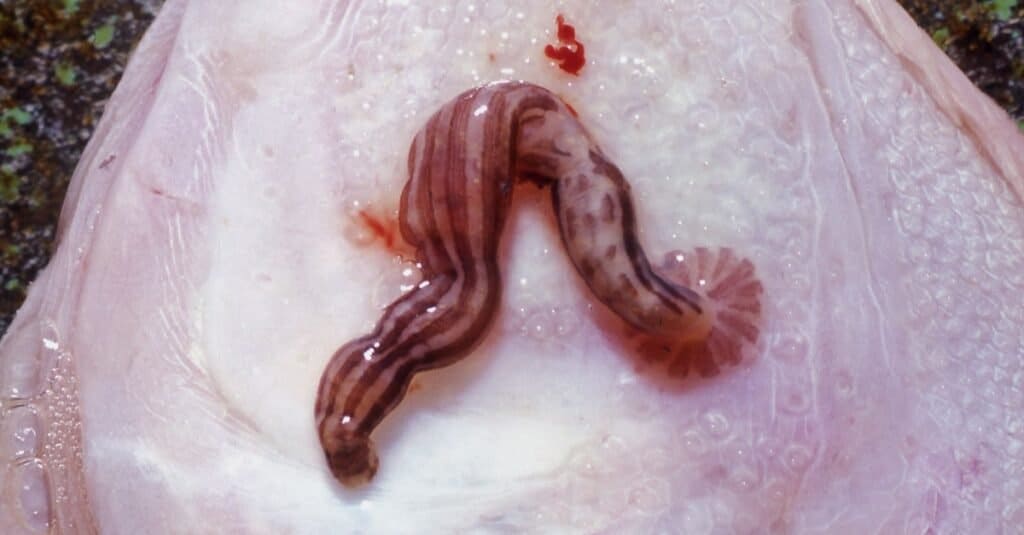
Although they are known for sucking blood, leeches have a varied diet. Although they suck blood, freshwater leeches also eat mollusks, insects, insect larvae, fish eggs, and worms. When they suck blood, they prefer to suck the blood of other aquatic creatures, including worms, snails, and fish.
Certain types of leeches are scavengers that feed on dead plant and animal life. Only a small fraction feed on the blood of mammals.
History and Evolution
While there are other parasitic animals in the world, leeches have evolved to be particularly successful at feeding well and eating undetected. The saliva of a leech is composed of about thirty different elements, which tells us that this is one of the most impressive adaptations of leeches. Over time, leeches have evolved saliva to paralyze their hosts and keep blood flowing freely.
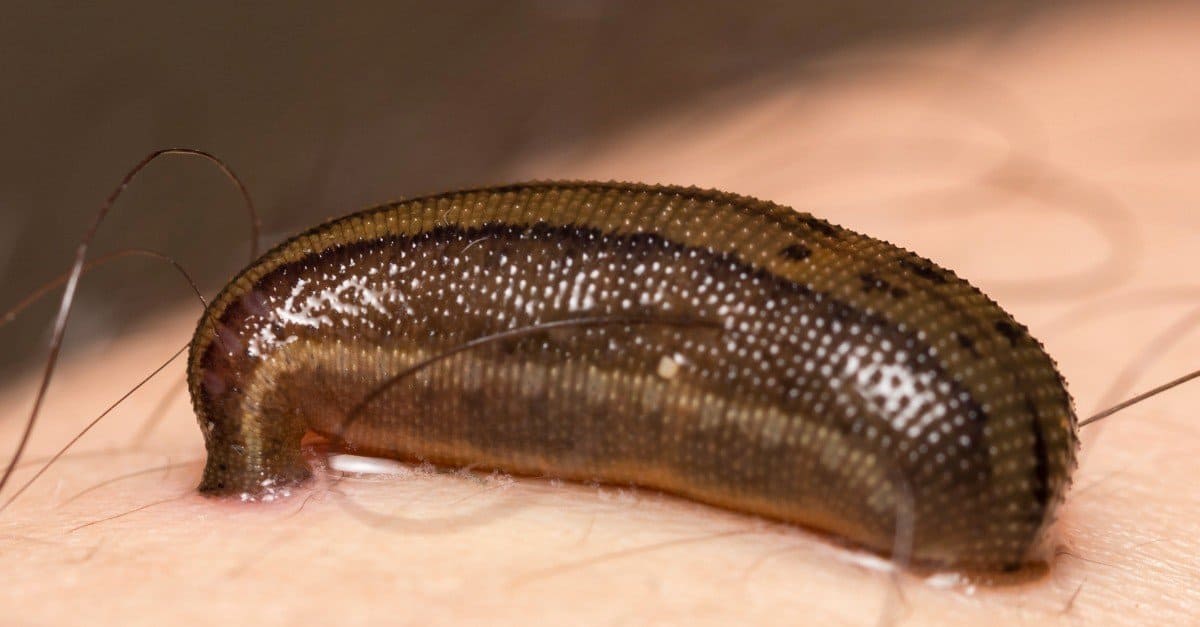
Predators and Threats
Leeches are an important food source for fish, turtles and ducks. Their population is stable and not vulnerable to any threats. Any activity that harms pond life will harm all types of leeches.

© iStock.com/kimetan
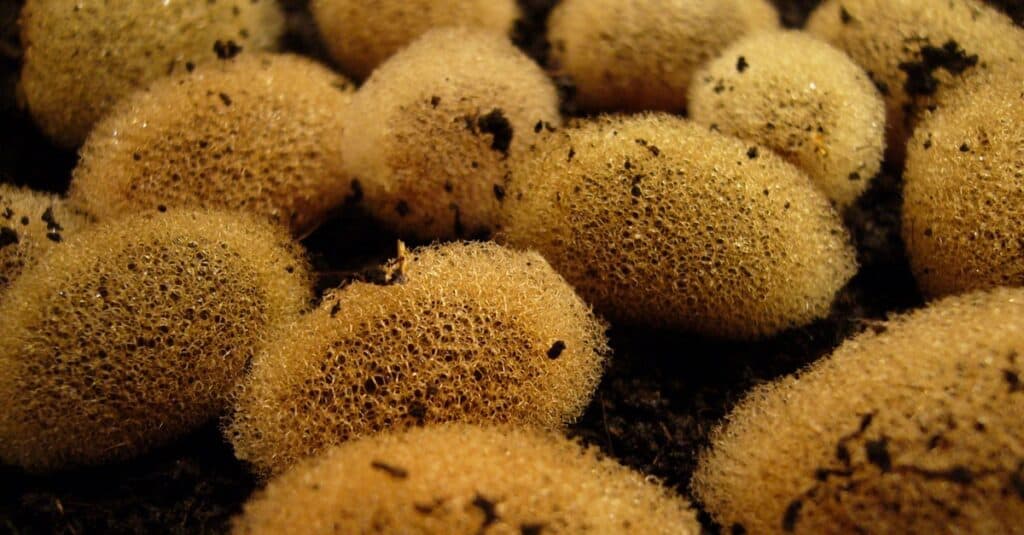
Reproduction and Life Cycle

© Ali Kiraz/Shutterstock.com
Leeches are hermaphroditic, there is no distinction between male and female. During reproduction, they use cross fertilization. Once the leeches' eggs are fertilized, the female lays them in cocoons. There may be anywhere from 1 to 300 eggs in the cocoon. The female then attaches the cocoon to a fixed location such as a plant or stone.
Small leeches develop inside cocoons. Unlike moths and butterflies, which go through multiple stages in a cocoon, they develop to full size. In some cases, the female leech wears a cocoon on her body for protection.
The development of pups inside the cocoon can take up to nine months. Leeches are born fully formed and can live independently. They reach sexual maturity within two years.
Where do leeches live compared to others of their kind? Leeches are solitary and only mingle with other leeches during breeding season.
They have a very long lifespan compared to many invertebrates. They can live up to 10 years in the wild. They live even longer in captivity.
population
There are no estimates for leech populations in the world. They live everywhere in the world except Antarctica, and their populations are not threatened.
Cute leeches?
We hope you've learned some interesting facts about these common, creepy but harmless animals. Like all animals, they play important roles in ecosystems. They may not be cute, but they're not dangerous.
See all 93 animals starting with L
It is a large, dark-colored worm related to earthworms. Its preferred habitat is warm, slow-moving bodies of water. A leech is a predator and blood-sucking parasite.
They're not dangerous, but spotting one on you can be unpleasant. Their bites are not painful because their saliva has an anesthetic. Unlike other biting insects, they do not carry venom or disease. You will bleed a lot because the anticoagulant in their blood stops the blood from clotting. It's not fun, but it's not dangerous either.
You may find one on your skin after wading or swimming in a pond or walking through a wet area. If you do so, follow these steps:
1. Locate the leech's mouth, which is the smallest end of its body.
2. Slide the nail under the leech's head towards the mouth, then push the head sideways. Some people use a sheet of paper or a thin, flat piece of wood.
3. It is safer to push the mouth open than to pull it open. Trying to pull off the leech could tear your skin.
4. Pull off the other end of the leech.
5. Throw away the leeches.
6. Wipe away the blood.
7. Wash the wound with warm soapy water.
8. Apply antibacterial ointment, iodine or hydrogen peroxide.
9. If the wound is bleeding, apply a bandage.
It bites you and sucks your blood.
Leeches can be beneficial. Because of their small teeth, they are useful in medicine. Medicinal leeches are specific species that doctors use during surgery and to treat certain conditions, including varicose veins, blood clots, and bacterial infections. The medical use of leeches is known as leech therapy.
not completely. A leech has 32 segments, each with its own part of the leech brain. It is a brain divided into 32 body parts.
Yes, you should delete them.
They mostly live in the shallow waters of lakes and ponds. Some live in jungle and wetland areas.
They are attracted to all animals that bleed.
Leeches cannot, but terrestrial species can.
It's easy to spot if someone is clinging to you. For quick identification, look for two tapered ends with suction cups. For accurate identification, look for a vampire at one end.





